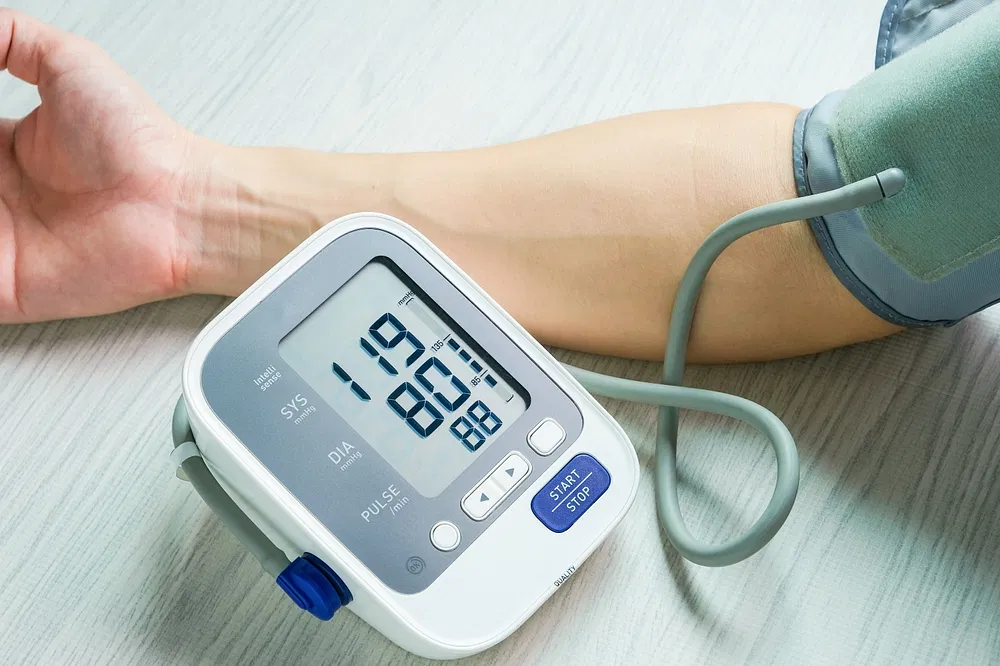
Introduction to Omega 3 and Its Importance
Omega-3 fatty acids have garnered significant attention in recent years, particularly regarding their role in supporting heart health and their potential to lower blood pressure. As a healthcare professional, I have observed a growing body of research that indicates omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to cardiovascular well-being. These essential fats are not produced by the body, making it imperative that we obtain them through our diet or supplementation. Research has shown that omega-3 fatty acids can effectively reduce triglycerides and inflammation, both of which are key factors in the development of cardiovascular diseases. By understanding the importance of omega-3, we can better appreciate their role in promoting heart health and managing blood pressure.
Mechanisms of Action in Blood Pressure Regulation
The mechanisms by which omega-3 fatty acids influence blood pressure regulation are multifaceted and compelling. Omega-3 supplementation may lower blood pressure effectively through several biological pathways. One of the primary ways is by improving endothelial function and promoting vasodilation, which is the widening of blood vessels. This effect can lead to reduced vascular resistance and lower blood pressure levels. Furthermore, a diet rich in omega-3 supports heart health by reducing inflammation, which is often a contributing factor to hypertension. Inflammatory processes can lead to arterial stiffness and increased blood pressure, so the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 are particularly beneficial. Overall, the evidence suggests that incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into our diets can play a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Review of Recent Clinical Trials
A review of recent clinical trials provides further evidence that omega-3 supplementation may lower blood pressure effectively. Numerous studies have aimed to quantify the effects of omega-3 fatty acids on blood pressure, and the results are promising. For instance, several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated that individuals who consume omega-3 supplements experience a significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure compared to those who do not. Additionally, research consistently shows that omega-3 fatty acids confer benefits for heart health and inflammation, further reinforcing their potential as a therapeutic intervention for managing hypertension. As a professional in the field, I find these findings encouraging, as they highlight the potential of omega-3 in not only lowering blood pressure but also enhancing overall cardiovascular health.
Dietary Sources and Recommended Intake
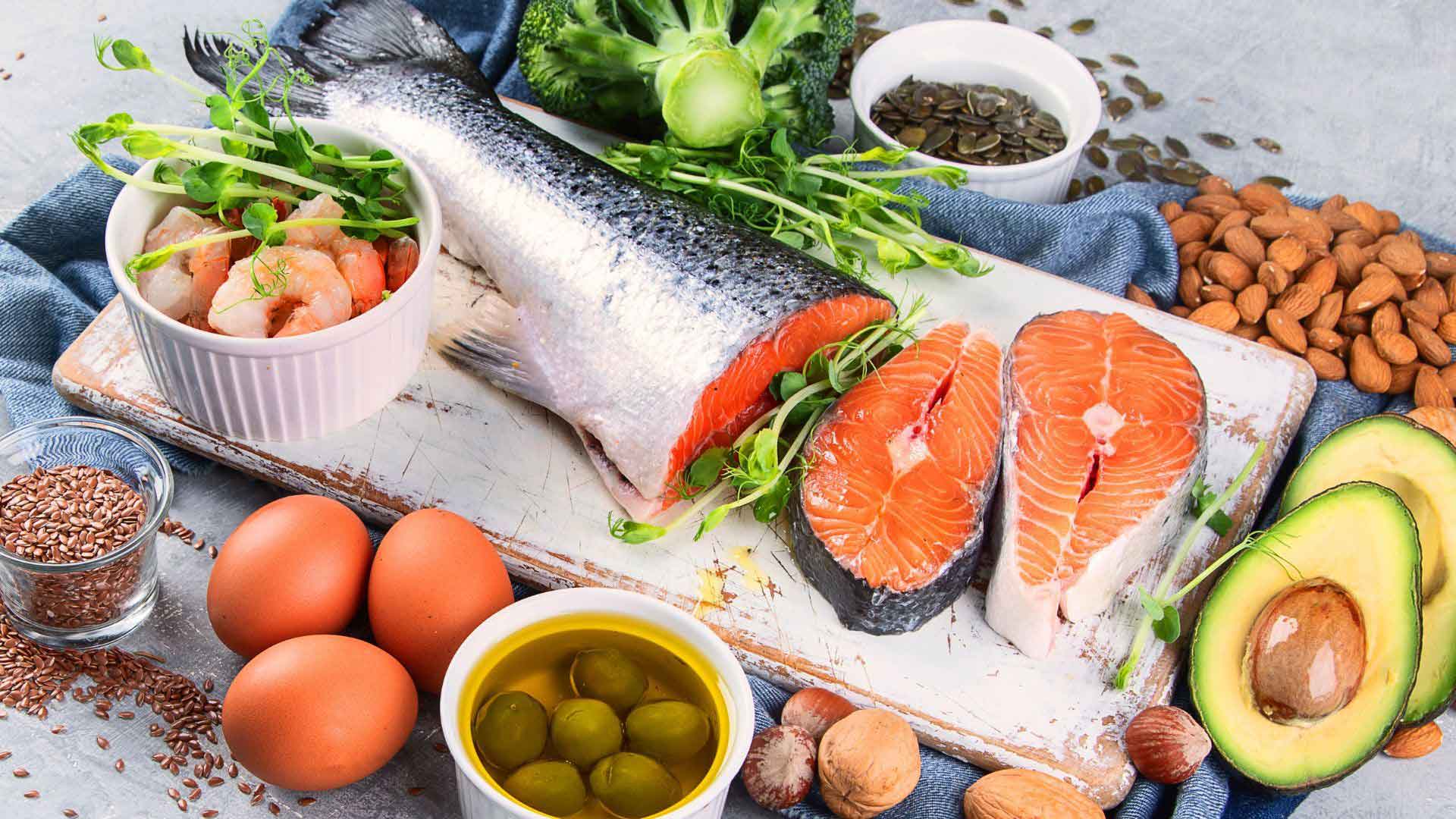
To effectively lower blood pressure, it is essential to incorporate omega-3 fatty acids into our diets. These beneficial fats are primarily found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids not only enhances heart health significantly but also provides a natural approach to managing blood pressure. The American Heart Association recommends at least two servings of fatty fish per week to achieve optimal omega-3 intake. For those who may not consume enough through diet alone, omega-3 supplements can be a viable option. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and form of supplementation, ensuring that individuals receive the maximum benefits for their cardiovascular health.
Conclusion and Future Research Directions
In conclusion, the research surrounding omega-3 fatty acids and their role in blood pressure regulation is both promising and essential for future exploration. While current studies indicate that omega-3 can effectively lower blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health outcomes, there is still much to learn. Future research should delve deeper into the specific mechanisms by which omega-3 fatty acids exert their effects on blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health. Additionally, it would be beneficial to investigate the long-term effects of omega-3 supplementation on various cardiovascular health outcomes, including heart disease and stroke risk. By expanding our understanding of omega-3, we can better inform individuals about their potential benefits and develop targeted strategies for managing hypertension and promoting heart health.
Recent Trends in Research on Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Blood Pressure

The relationship between omega-3 fatty acids and blood pressure has garnered significant attention in the scientific community over the past few years. As we delve into the latest trends in this area, we can identify both popular research themes and underexplored areas that warrant further investigation.
Popular Research Areas
1. Mechanisms of Action: A significant amount of recent research has focused on understanding the mechanisms by which omega-3 fatty acids influence blood pressure. Studies have explored how these fatty acids can improve endothelial function, reduce inflammation, and modulate autonomic nervous system activity. Researchers are particularly interested in the roles of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in these processes.
2. Dietary Sources and Supplements: There has been an ongoing debate about the effectiveness of dietary sources of omega-3s (like fish and flaxseed) versus supplements (like fish oil capsules). Recent meta-analyses have indicated that while both sources can be beneficial, the bioavailability and the impact on blood pressure may differ. This has led to a surge in studies comparing the effects of various omega-3 formulations.
3. Population Studies: Epidemiological studies have consistently shown a correlation between higher omega-3 intake and lower blood pressure across different populations. Recent research has expanded this focus to include diverse demographic groups, examining how genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors influence the relationship between omega-3s and blood pressure.
4. Omega-3 and Hypertension Subtypes: There is growing interest in how omega-3 fatty acids may affect different subtypes of hypertension, such as resistant hypertension or hypertension related to metabolic syndrome. Understanding these nuances could lead to tailored dietary recommendations and interventions.
5. Clinical Trials: Numerous clinical trials are underway to assess the efficacy of omega-3 supplementation in managing hypertension. These trials often examine various dosages, forms of omega-3s, and durations of treatment, providing a wealth of data that may refine clinical guidelines.
Underexplored Areas
1. Long-term Effects: While short-term studies have provided valuable insights, there is a lack of long-term research examining the sustained effects of omega-3s on blood pressure. Understanding the long-term implications of omega-3 intake could be crucial for developing effective dietary guidelines.
2. Interaction with Other Nutrients: The interplay between omega-3 fatty acids and other dietary components (like omega-6 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals) is an area that has not received sufficient attention. Research into how these interactions may affect blood pressure could open new avenues for dietary interventions.
3. Individual Variability: The variability in individual responses to omega-3 supplementation is an underexplored area. Factors such as genetics, age, sex, and existing health conditions can influence how effective omega-3s are in lowering blood pressure. More personalized approaches to supplementation could enhance outcomes.
4. Psychological Factors: Emerging research suggests that psychological factors, such as stress and depression, may influence blood pressure and could interact with omega-3 intake. Exploring this relationship could lead to a more holistic approach to managing hypertension.
5. Omega-3 Index: The omega-3 index, a measure of the amount of EPA and DHA in red blood cell membranes, is gaining traction as a potential biomarker for cardiovascular health. More research is needed to establish its relationship with blood pressure and overall cardiovascular risk.
Conclusion
The exploration of omega-3 fatty acids and their impact on blood pressure is a vibrant and evolving field. While significant strides have been made in understanding their benefits, particularly regarding mechanisms, dietary sources, and population studies, there remain crucial gaps that researchers are beginning to address. By focusing on long-term effects, nutrient interactions, individual variability, psychological factors, and the omega-3 index, future research could provide a more comprehensive understanding of how to leverage omega-3s for optimal blood pressure management. As this field progresses, it holds the potential to inform dietary guidelines and improve cardiovascular health outcomes for diverse populations.
- Vaping vs Smoking: Health Risks Revealed - July 29, 2025
- Hypertension Management with Captopril: Weighing Risks of Adverse Effects - July 22, 2025
- Biotin Side Effects: Hair Growth Troubles and Skin Rash Risks - July 15, 2025